Artificial intelligence has taken a great leap with the help of Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), a method that combines the power of human judgment with traditional machine learning. Unlike conventional training processes that depend entirely on static datasets, RLHF uses human input to make AI systems more adaptable and contextually aware.
What Makes RLHF Unique?
RLHF uses direct human feedback, enabling AI to refine its actions based on human evaluations. Reinforcement Learning involves teaching an agent to make decisions by exploring an environment and learning from the rewards or penalties it receives.
Foundations of Reinforcement Learning
To know more about RLHF, it’s important to first understand the basic terminologies of Reinforcement Learning:
- Agent: The entity making decisions or learning.
- Environment: The setting where the agent operates, providing feedback based on its actions.
- Actions: Choices available to the agent, defined by the “action space.” • State: The current situation or snapshot of the environment as perceived by the agent. • Reward: Positive or negative feedback the agent receives for its actions. • Policy: A strategy the agent uses to decide its next action.
- Value Function: An estimate of the benefits of a particular state or action based on future rewards.
By combining these elements, traditional Reinforcement Learning focuses on teaching agents to achieve long-term goals. RLHF enhances this by introducing human feedback as a key part of the reward mechanism.
Working of RLHF
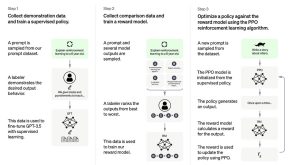
RLHF is typically implemented in three phases:
- Foundation Model: Training starts with a pre-trained model, which saves time and resources.
- Human Feedback: Human evaluators assess the AI’s outputs, assigning scores based on quality, relevance, or ethical considerations.
- Reinforcement Learning: The AI is fine-tuned using this feedback, enabling iterative improvements in its responses.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, RLHF is not without challenges:
- Subjectivity in Feedback: Human evaluators may provide biased or inconsistent feedback.
- Ethical Concerns: If feedback comes from a non-diverse group, the AI may adopt some biased behaviours.
- Scalability Issues: Gathering quality human feedback at scale is both time-consuming and costly.
Conclusion
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) represents a shift in AI training, emphasizing collaboration between humans and machines. By integrating human feedback into the learning process, RLHF enhances AI performance to a great extent. As this technology evolves, it holds the promise of creating AI that truly understands humans.
 End to End Technology Solutions
End to End Technology Solutions
