Table of contents
- Definition
- Conceptual Implementation
- Java Code & Explanation
- Applications of DFS
Definition
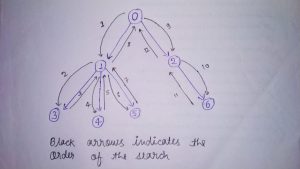
Depth First Search (DFS) is an algorithm for traversing Graph Data Structure. The algorithm starts at some arbitrary node in the graph and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.
Stack Data structure is needed to keep track of the nodes discovered so far along a specified branch which helps in backtracking the graph.
Conceptual Implementation
Java Code & Explanation
import java.util.*;
class Main{
public static class Graph{
int vertices; // Number of vertices
LinkedList<Integer> adj[]; // Array of linked list to store the Edges of the graph
// Constructor of the Graph
Graph(int v){
vertices = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v]; // Initialization of the array with size of vertices
for(int i=0; i<vertices; i++){
adj[i] = new LinkedList<>(); // Initialize linked list object on every index of the array
}
}
// Make Edge between u and v vertices
void addEdge(int u, int v){
adj[u].add(v);
}
/*
First mark the sourceNode as visited
Print the Node
Iterate through all its neighbor until all the node marked as visited
*/
void DFS(int sourceNode, boolean[] visited){
visited[sourceNode] = true;
System.out.print(sourceNode + " ");
Iterator<Integer> iterator = adj[sourceNode].listIterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
int neighbourToSourceNode = iterator.next();
DFS(neighbourToSourceNode, visited);
}
}
// Util Method
void DFSUtil(int sourceNode){
boolean visited[] = new boolean[vertices]; // Array to store marked visited vertices
DFS(sourceNode, visited); // Call DFS Method
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graph graph = new Graph(7);
graph.addEdge(0, 1);
graph.addEdge(0, 2);
graph.addEdge(1, 3);
graph.addEdge(1, 4);
graph.addEdge(1, 5);
graph.addEdge(2, 6);
extracted(graph);
}
private static void extracted(Graph graph) {
graph.DFSUtil(0);
}
}
Output
![]()
Applications
- Topological Sorting
- Scheduling Problem
- Cycle detection in graph
- Maze Problem
- Sudoku Puzzle
 End to End Technology Solutions
End to End Technology Solutions
