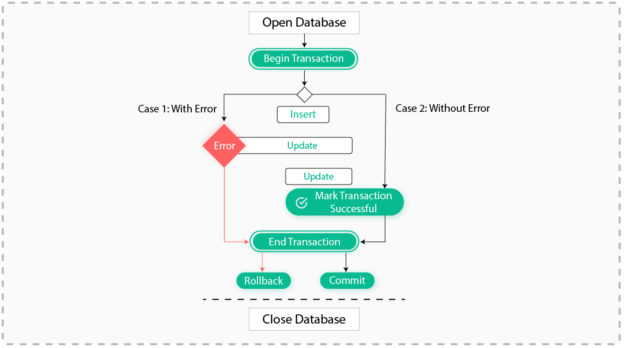
This blog is about database transaction handling and its design pattern in android. It also gives a brief knowledge on how to handle Exception.
Here we have a main method which is responsible to get database instance -> start Database Transaction -> Mark Transaction Successful -> Commit or Rollback Transaction -> Close database. This main method have its two child method both methods perform some database transaction
1 . Main method defines Transaction boundaries.
2. Methods joins the Database transaction.
3. Another Method joins the Database Transaction.
1 . Main method defines Transaction boundaries :
This method will:
- Get Database instance.
- Start Database Transaction.
- Mark Transaction Successful.
- Commit or Rollback Transaction.
- Close Database.
public static void prepareData() throws <Name of the app>AppException
{
try
{
//Get Database Instance
sqliteDatabase = DBUtils.openWritableDatabase();
//Start Database Transaction
DBUtils.beginTransaction(sqliteDatabase);
prepareData1(sqLiteDatabase);
prepareData2(sqLiteDatabase);
//Mark Transaction Successful
setTransactionSuccessful(sqLiteDatabase);
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
String exceptionMessage = "Error in inserting data."
ExceptionManager.processException(AppConstant.ERROR_CODE_1015,
exceptionMessage, exception);
}
finally
{
//Commit or Rollback transaction
endTransaction(sqLiteDatabase);
//Close Database
appDatabase.closeDatabase();
}
}
1.1 Get Database Instance
- DbUtils.openWritableDatabase() – If our requirement is to fetch the data from database , we have to use openWritableDatabase() method.
In DbUtil class create openWritableDatabase()
/**
* Opens the database
* @return
*/
public static SQLiteDatabase openWritableDatabase()
{
SQLiteDatabase sqliteDatabase = null;
// Opening new database
sqliteDatabase = sqliteOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
//Enable Write Ahead Logging
sqliteDatabase.enableWriteAheadLogging();
return sqliteDatabase;
}
- DbUtils.openReadableDatabase() – If our requirement is to read the data from database use openReadableDatabase() method.
In DbUtil class create openReadableDatabase()
/**
* Opens the database
* @return
*/
public static SQLiteDatabase openReadableDatabase()
{
SQLiteDatabase sqliteDatabase = null;
// Opening new database
sqliteDatabase = sqliteOpenHelper.getReadableDatabase();
return sqliteDatabase;
}
1.2 Start Database Transaction
- beginTransaction(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase) – This method is used to begin our transaction in EXCLUSIVE mode and when parent transaction is completed all child transactions will be rollback or commit ed.
In DbUtils class create beginTransaction() method:
public static void beginTransaction(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase)
{
try
{
if(sqLiteDatabase != null)
{
sqLiteDatabase.beginTransaction();
}
}
catch(Exception exception)
{
//Consume Exception
}
}
1.3 Mark Transaction Successful:
- setTransactionSuccessful(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase) method is used to mark our transaction successful. All database related task must be only done between beginTransaction() method and setTransactionSuccessful(SQLiteDatabase sqliteDatabase) method.Do not do any database related task between setTransactionSuccessful(SQLiteDatabase sqliteDatabase) method and endTransaction(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase) method.
In DbUtils class createsetTransactionSuccessful(SQLiteDatabase sqliteDatabase) :
public static void setTransactionSuccessful(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase)
{
try
{
if(sqLiteDatabase != null)
{
sqLiteDatabase.setTransactionSuccessful();
}
}
catch(Exception exception)
{
//Consume Exception
}
}
1.4 Commit or Rollback Transaction
- endTransaction(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase) – This method is used to commit or rollback our database transaction.If our transaction is marked successful by setTransactionSuccessful() method then our transaction will be commited else all changes will be rollback.
In DbUtils class create endTransaction(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase) method :
public static void endTransaction(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase)
{
try
{
if(sqLiteDatabase != null)
{
sqLiteDatabase.endTransaction();
}
}
catch(Exception exception)
{
//Consume Exception
}
}
1.4 Close Database.
//Close Database appDatabase.closeDatabase();
2 . Method joins the Database Transaction
This is the child transaction of prepareData() method here SQLiteDatabase object must be passed from parent transaction method .
- Exceute query.
- Handle Exception
private static void prepareData1(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase)
throws <Name of the app>AppException
{
ContentValues contentValues = null;
long rowId = 0;
try
{
//Prepare ContentValues object
contentValues = new ContentValues();
//Execute Query
rowId = sqLiteDatabase.insertOrThrow("Table Name", null, contentValues);
//If rowId is -1 then this means that Row was not inserted.
//Something went wrong. Throw Exception
if (rowId == -1)
{
String exceptionMessage = "Error in inserting Data. Row Id is -1.";
throw new <Name of the App>AppException
(AppConstant.ERROR_CODE_1011, exceptionMessage);
}
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
//Handle Exception
String exceptionMessage = "Error in inserting Data.";
int errorCode = AppConstant.ERROR_CODE_8012;
ExceptionManager.dispatchExceptionDetails(errorCode, message, exception);
}
2.1 Execute Query
Here we are inserting data in database and after execution of query we have to check whether our data is inserted or not. If our data is not inserted thow AppException.
//Execute Query
rowId = sqLiteDatabase.insertOrThrow("Table Name", null, contentValues);
//If rowId is -1 then this means that Row was not inserted.
//Something went wrong. Throw Exception
if (rowId == -1)
{
String exceptionMessage = "Error in inserting Data. Row Id is -1.";
throw new <Name of the App>AppException
(AppConstant.ERROR_CODE_1011, exceptionMessage);
}
2.2 Handle Exception
catch (Exception exception)
{
//Handle Exception
String exceptionMessage = "Error in inserting Data.";
int errorCode = AppConstant.ERROR_CODE_8012;
ExceptionManager.dispatchExceptionDetails(errorCode, message, exception);
}
ExceptionManager.dispatchExceptionDetails(errorCode, message, exception) method is used to throw or create AppException object.
public static void dispatchExceptionDetails(int exceptionCode, String exceptionMessage, Exception exceptionObject) throws <Name of the App>AppException
{
if(exceptionObject instanceof AppException)
{
throw (AppException) exceptionObject;
}
else
{
//Log Exception details
logException(exceptionCode, exceptionMessage, exceptionObject);
//Throw Exception
throw new <Name of the App>AppException(exceptionCode, exceptionMessage);
}
}
3 . Another Method joins the Database Transaction
private static void prepareData2(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase)
throws <Name of the app>AppException
{
ContentValues contentValues = null;
long rowId = 0;
try
{
contentValues = new ContentValues();
//Prepare ContentValues object
rowId = sqLiteDatabase.insertOrThrow("Table Name", null, contentValues);
//If rowId is -1 then this means that Row was not inserted.
//Something went wrong. Throw Exception
if (rowId == -1)
{
String exceptionMessage = "Error in inserting Data. Row Id is -1.";
throw new <Name of the App>AppException
(AppConstant.ERROR_CODE_1013, exceptionMessage);
}
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
//Handle Exception
String exceptionMessage = "Error in inserting Data.";
int errorCode = AppConstant.ERROR_CODE_8012;
ExceptionManager.dispatchExceptionDetails(errorCode, message, exception);
}
}
 End to End Technology Solutions
End to End Technology Solutions